Search Strategies
In AI problems, it is important to use search strategies to find the goal in them.
Search Types
Uniformed Search (Blind Search) 盲目搜索
No other information like path cost or the number of steps are given. Only could it do is to distinguish from goal state from non-goal state.- Types
- Breadth-first Search
- Uniform-cost Search
- Depth-first Search
- Depth-limited Search
- Iterative Deeping Search
- Bidirectional Search
- Types
Informed Search (Heuristic Search) 启发式搜索
Giving some other information to help finding the goal state.
Performance Measurement
Completeness 完成性
Whether the algorithm guarantee to find the solution if there is any.Optimality 最优性
Whether the algorithm could find the optimal solution.Time Complexity 时间复杂度
Time cost of the algorithm.Space Complexity 空间复杂度
Memory cost of the algorithm.
O-natation
$O(g(n))={f(n): \text{there exist positive constants } c \text{ and } n_0 \text{ such that for all } n>=n_0}$
*i.e. When $n>=n_0, f(n)<=cg(n).$
$g(n)$ is an asymptotic upper bound (渐进上界) for $f(n)$. If $f(n) \in O(g(n))$, we write $f(n)=O(g(n))$.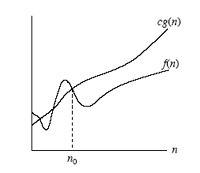
*$g(n)$ is a set of functions.
*O stand for the order of growth of $f(n)$. O 的含义是 $f(n)$ 的数量级,$g(n)$ 是算法中基本运算的频度。
Breadth-first Search
Search every node in the certain level before going to next level.
Branching Factor: The maximum number of children for each internal node in a tree.
Suppose the branching factor is 2. When the solution node is at the level $d+1$, it should expand the maximum number of node to be $1+2+2^2+2^3+...+2^d=2^{d+1}-1=O(2^d)$.
Advantages
- Complete (It is guarantee to find solution if there is any)
- Always find the shallowest goal first when there are multi-solutions.
Drawback
- Memory and time cost may not support due to it must maintained all the nodes in memory at the same time.
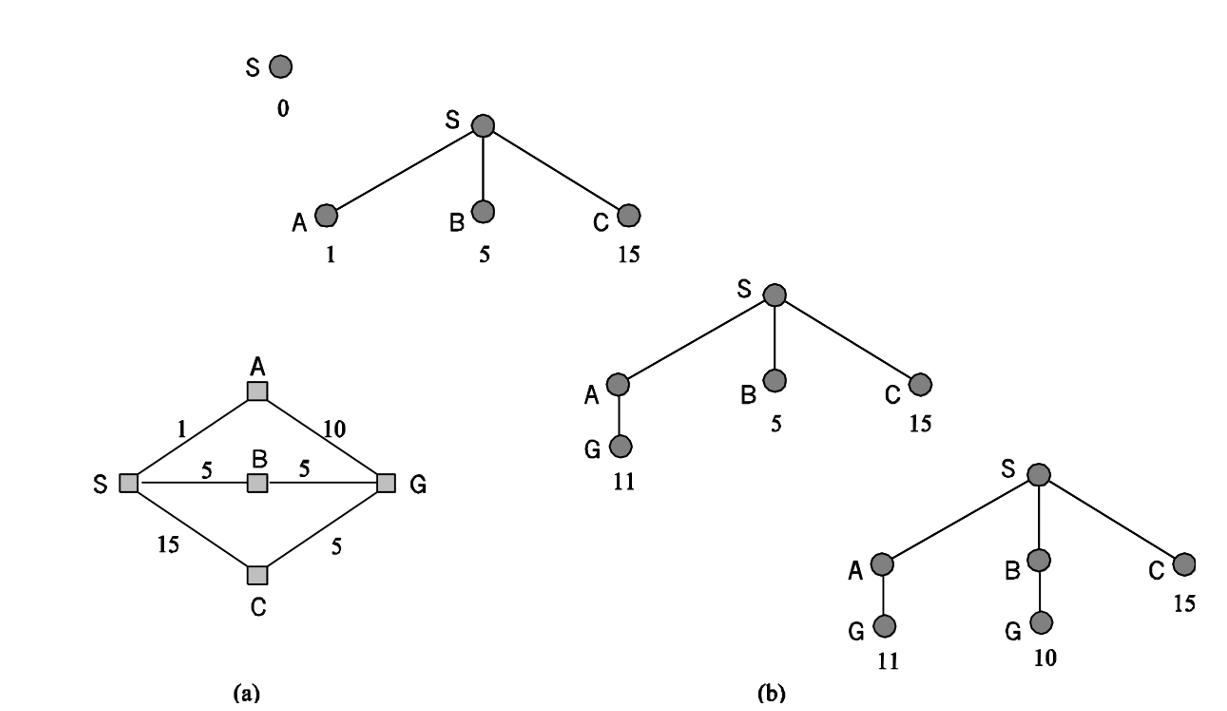
Uniform Cost Search
- Modifies the Bread-first search strategy by always expanding the lowest-cost node.
- The first solution found is guaranteed to be the cheapest solution.
Depth-first Search
Depth-first search always expands the node at the deepest level of the tree.
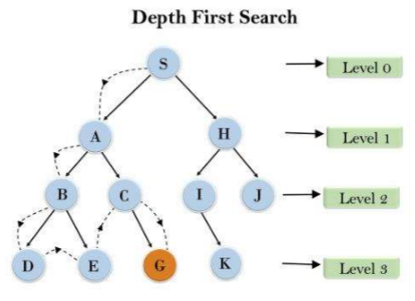
Advantages
- Have modest memory Requirement. Only store a single path from the root to a leaf node, along with the remaining unexpanded sibling nodes for each node on the path. For branch factor $b$ and maximum depth $m$, it only need $bm$ nodes to storage.
- Time complexity is $O(b^m)$.
Drawbacks
- May stuck when going down the wrong path (infinite loop).
- May find a solution path longer than optimal solution.
- Neither complete nor optimal.
References
[1] Y.M. Cheung. COMP 7015 Artificial Intelligence. Hong Kong Baptist University, 2020
[2] 王道论坛.2020 年数据结构考研复习指导[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2019